The DC-DC converter in an electric vehicle (EV) is a crucial component that efficiently converts the high voltage from the main battery to the lower voltage needed for accessories like lights, infotainment, and power steering, ensuring all vehicle systems operate smoothly and safely.
Thinking about an electric vehicle? It’s an exciting step, and you’re probably curious about all the cool technology that makes them tick. One piece of that puzzle, often hidden away, is the DC-DC converter. You might hear this term and wonder, “What exactly does it do, and why is it so important for my EV?” It’s a fair question, and understanding it can demystify some of the magic behind your electric ride. Don’t worry, it’s not as complicated as it sounds! We’re here to break it down in a way that makes perfect sense, helping you feel more confident about your EV knowledge. Let’s dive in and discover the essential role of the DC-DC converter.
Contents
- 1 Unpacking the DC-DC Converter in Your Electric Vehicle
- 2 Why is a DC-DC Converter Essential for EVs?
- 3 How Does a DC-DC Converter Work?
- 4 The DC-DC Converter’s Role in EV Charging
- 5 Key Components and How They Work Together
- 6 Benefits of Efficient DC-DC Conversion in EVs
- 7 Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- 8 DC-DC Converters vs. Traditional Cars
- 9 The Future of DC-DC Converters in EVs
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Unpacking the DC-DC Converter in Your Electric Vehicle
So, you’ve got your shiny new electric car, and you’re enjoying the smooth, quiet ride. But have you ever wondered how all those everyday things inside your car – the lights, the radio, the power windows, even the little screen that shows your speed – get the power they need? Electric vehicles have a big, powerful battery that stores a lot of energy, usually at a high voltage. This high voltage is fantastic for driving the wheels, but it’s way too much for the smaller, everyday systems in your car. That’s where the unsung hero, the DC-DC converter, comes in.
Think of it like a smart adapter. Your EV’s main battery is like a super-powerful, high-voltage outlet. But your car’s interior electronics and accessories are like your phone or laptop – they need a different, lower voltage to work safely and efficiently. The DC-DC converter acts as that essential bridge, taking the high-voltage Direct Current (DC) power from the main battery and stepping it down to a lower DC voltage, typically around 12 volts, which is the standard for most automotive accessories. Without it, those everyday conveniences would either be overloaded and fry, or they wouldn’t work at all!
Why is a DC-DC Converter Essential for EVs?
The importance of the DC-DC converter in an electric vehicle cannot be overstated. It’s not just a helpful add-on; it’s a fundamental necessity for the safe and efficient operation of the entire vehicle. Let’s break down its key roles:
- Powering Auxiliary Systems: As mentioned, the primary function is to supply lower voltage power to all the vehicle’s auxiliary systems. This includes everything from your headlights, taillights, and interior lighting to your infotainment system, navigation, power steering, climate control (AC and heating), power windows, door locks, and the car’s 12V battery itself (which starts up the car and powers the initial electronics).
- Charging the 12V Battery: EVs still have a 12V battery, much like traditional gasoline cars. This 12V battery is crucial for starting up the vehicle’s computers and control systems before the main high-voltage battery is engaged. The DC-DC converter continuously charges this 12V battery from the main high-voltage battery, ensuring it’s always ready to go.
- Voltage Regulation and Stability: The DC-DC converter doesn’t just step down voltage; it also regulates it. This means it provides a stable, consistent voltage supply to the accessories, preventing fluctuations that could damage sensitive electronic components.
- Efficiency and Range: By efficiently converting the high-voltage power, the DC-DC converter minimizes energy loss. This improved efficiency directly contributes to maximizing the vehicle’s driving range on a single charge. A less efficient converter would waste more energy as heat, reducing how far you can drive.
- Safety: Converting high voltages to lower, safer voltages is a critical safety feature. It isolates the lower-voltage systems from the high-voltage main battery, protecting occupants and the vehicle’s electronics from potential electrical hazards.
How Does a DC-DC Converter Work?
The magic behind the DC-DC converter lies in a few core electronic principles. While the inner workings can get quite technical, we can understand the basic idea without needing an engineering degree!
At its heart, a DC-DC converter uses electronic switches (like transistors) that turn on and off very rapidly. This rapid switching creates a form of alternating current (AC) from the initial DC power. This “chopped-up” DC is then passed through a transformer, which can easily change the voltage level (step it up or down). Finally, another set of switches and filters convert the changed AC voltage back into a stable, lower-voltage DC output.
There are different types of DC-DC converters, but in EVs, you’ll commonly find:
| Converter Type | Description | Common EV Application |
|---|---|---|
| Buck Converter | Steps voltage down. | Primary function for reducing high battery voltage to 12V. |
| Boost Converter | Steps voltage up. | Less common for the main accessory supply, but can be used in specific power management scenarios. |
| Buck-Boost Converter | Can both step voltage up or down. | Offers flexibility but can be more complex. |
The converter is typically managed by the vehicle’s control unit, which monitors the voltage demands of various systems and adjusts the converter’s operation accordingly. It’s a sophisticated piece of engineering designed for maximum efficiency and reliability.
The DC-DC Converter’s Role in EV Charging
While the DC-DC converter’s primary job is to power the car’s internal systems from the main battery, it also plays a subtle but important role during charging. When your EV is plugged in, the charging system delivers AC power (from your home or a public charger) to the car’s onboard charger. The onboard charger converts this AC power into DC power, which then charges the main high-voltage battery.
However, during this process, the DC-DC converter is still active. It continues to draw power from the main battery (or the onboard charger’s DC output) to power the vehicle’s 12V systems. This ensures that your car’s lights, computer systems, and other accessories remain operational while it’s plugged in and charging. Without the DC-DC converter, you wouldn’t be able to use the infotainment system or even turn on the interior lights while the car is connected to a charger, which would be quite inconvenient!
Key Components and How They Work Together
To truly appreciate the DC-DC converter, let’s look at its main parts and how they interact within the EV’s electrical architecture:
- Input Terminals: These connect directly to the high-voltage battery pack. They receive the raw, high-voltage DC power.
- Switching Elements: These are the heart of the converter – typically high-speed transistors like MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors). They switch the input voltage on and off at extremely high frequencies (tens or hundreds of kilohertz).
- Inductors: These are coils of wire that store energy in a magnetic field when current flows through them. They help smooth out the pulsed power from the switching elements and store energy that is then released at a different voltage level.
- Capacitors: These store electrical energy in an electric field. They are used to filter out voltage ripples and provide a stable DC output.
- Transformer (in some designs): Used to step voltage up or down by electromagnetic induction. The turns ratio of the transformer dictates the voltage change.
- Control Circuitry: This is the “brain” of the converter. It monitors the output voltage and adjusts the switching frequency or duty cycle (how long the switches are on) to maintain the desired output voltage, even as the input voltage or load changes.
- Output Terminals: These deliver the regulated, lower-voltage DC power to the vehicle’s 12V electrical system.
The interplay between these components is crucial. For instance, a buck converter uses a switch, an inductor, and a capacitor. When the switch is on, current flows through the inductor, storing energy. When the switch turns off, the inductor releases its stored energy, and the capacitor smooths out the resulting voltage to provide a steady output. The control circuitry ensures this process happens precisely to meet the demand.
Benefits of Efficient DC-DC Conversion in EVs
The drive for efficiency in electric vehicles is paramount, and the DC-DC converter is a key player in achieving this. Here are the main benefits:
- Extended Driving Range: Every bit of energy saved by an efficient DC-DC converter translates directly into more miles on the road. Less wasted energy means more energy available to power the electric motor.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: An efficient converter means less overall energy is drawn from the main battery for auxiliary systems, lowering the vehicle’s total energy consumption.
- Longer Component Lifespan: Stable and regulated voltage prevents stress on the sensitive electronic components that rely on the lower voltage supply. This can lead to fewer component failures and a more reliable vehicle.
- Lower Heat Generation: Inefficient converters generate more heat as a byproduct of wasted energy. Efficient designs minimize this heat, reducing the need for complex and energy-consuming cooling systems for the converter itself.
- Cost Savings: While not directly visible to the driver, improved efficiency and reliability can contribute to lower maintenance costs over the life of the vehicle.
Manufacturers invest heavily in optimizing their DC-DC converters. Companies like Infineon Technologies and Texas Instruments are at the forefront of developing advanced semiconductor solutions that enable these highly efficient converters. You can learn more about the advancements in power electronics at resources like the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers), a leading professional organization in the field.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
While DC-DC converters are designed for reliability, like any electronic component, they can sometimes encounter issues. Because they are integrated deep within the vehicle’s systems, diagnosing problems often requires specialized tools and knowledge.
Symptoms of a Failing DC-DC Converter:
- Malfunctioning Accessories: Lights flickering, infotainment system cutting out, power windows failing, or the power steering becoming erratic are all potential signs.
- Dashboard Warning Lights: The vehicle’s diagnostic system will likely detect a fault and illuminate a warning light, often related to the electrical system or battery.
- 12V Battery Not Charging: If the DC-DC converter fails to charge the 12V battery, you might experience issues starting the car or powering up the initial electronic systems.
- Reduced Driving Range: While less direct, a severely malfunctioning converter that causes significant energy waste could theoretically impact range.
What to Do If You Suspect a Problem:
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s best to:
- Consult Your Owner’s Manual: It may offer basic troubleshooting steps or explain specific warning lights.
- Contact a Certified EV Technician: Due to the high voltages involved and the complexity of EV systems, it’s crucial to have any suspected issues diagnosed by a qualified professional. They have the specialized equipment to safely test the converter and related systems. Attempting DIY repairs on high-voltage EV components can be extremely dangerous.
For more general information on EV maintenance and safety, resources like the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy offer valuable insights.
DC-DC Converters vs. Traditional Cars
It’s interesting to compare how EVs and traditional gasoline cars handle power distribution. In a gasoline car, the alternator, driven by the engine, is responsible for generating electricity to power the car’s accessories and recharge the 12V battery. The engine’s speed directly influences the alternator’s output.
In an EV, the situation is different:
| Feature | Electric Vehicle (EV) | Traditional Gasoline Car |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Power Source for Accessories | High-voltage battery, converted by DC-DC converter to 12V. | Alternator, driven by the engine, directly supplies 12V. |
| 12V Battery Charging | DC-DC converter draws from high-voltage battery. | Alternator recharges the 12V battery. |
| Efficiency | DC-DC converters are highly efficient, minimizing energy waste. | Alternator efficiency can vary with engine RPM; some energy is lost to engine load. |
| System Complexity | Requires sophisticated power electronics for voltage conversion. | Relatively simpler system, but dependent on engine operation. |
The key difference is that EVs decouple the power supply for accessories from the direct operation of an internal combustion engine. The DC-DC converter provides a stable, efficient, and independent power source, allowing for precise control and optimization of energy usage, which is fundamental to the EV’s design philosophy.
The Future of DC-DC Converters in EVs
The evolution of electric vehicles is rapid, and so is the technology within them. DC-DC converters are no exception. We’re seeing continuous advancements aimed at making them even more efficient, compact, and integrated.
- Higher Efficiency Ratings: Manufacturers are pushing for converters that lose even less energy during the conversion process, further extending EV range.
- Integrated Systems: In some future designs, the DC-DC converter might be more tightly integrated with other power electronics, such as the onboard charger or the motor inverter, leading to smaller, lighter, and potentially more cost-effective solutions.
- Bidirectional Capability: While most current EV DC-DC converters are unidirectional (high voltage to low voltage), future systems might incorporate bidirectional capabilities. This could allow the 12V system to temporarily support the main battery in certain scenarios or enable more advanced vehicle-to-grid (V2G) functionalities.
- New Materials and Architectures: Research into new semiconductor materials (like Silicon Carbide or Gallium Nitride) and innovative converter architectures promises higher power density, better thermal performance, and improved reliability.
These ongoing developments mean that the humble DC-DC converter will continue to be a critical, evolving component in making electric vehicles more practical, affordable, and appealing to a wider audience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the main job of a DC-DC converter in an EV?
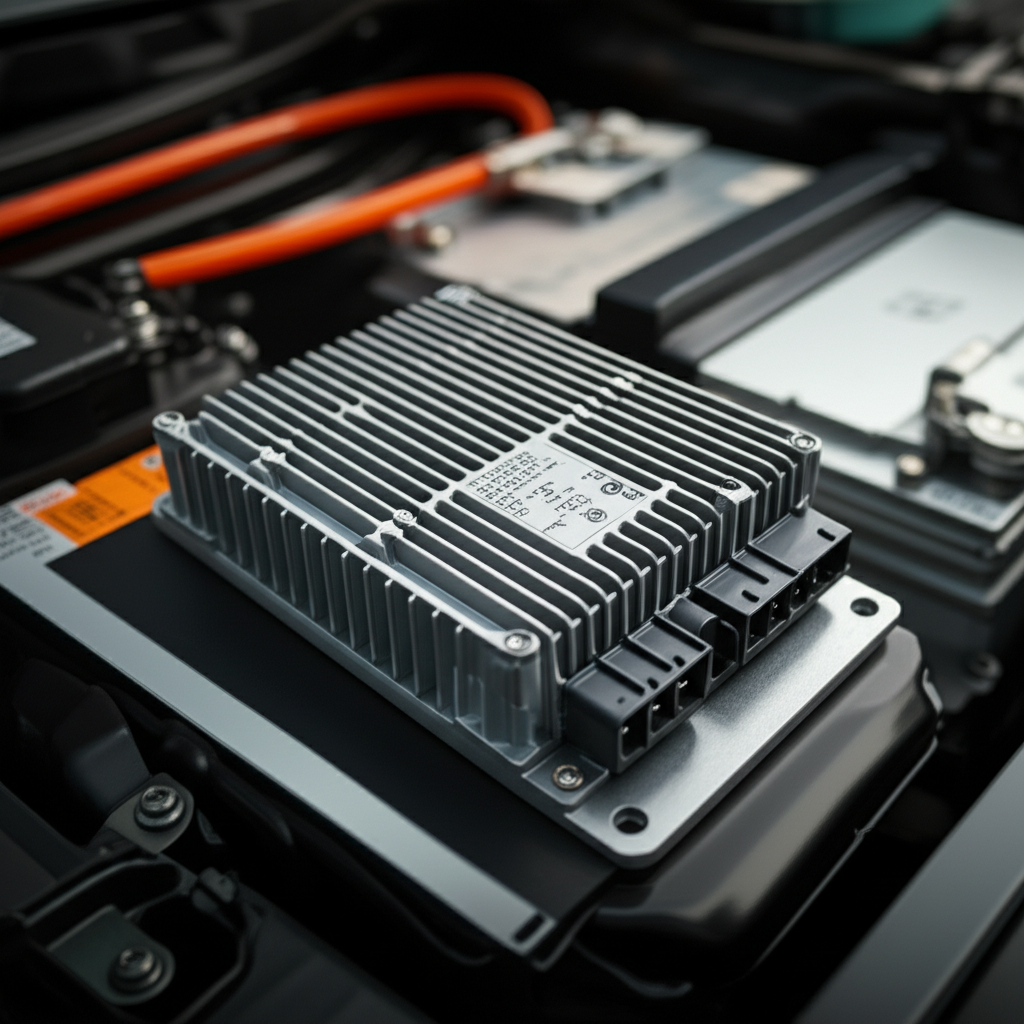
The main job of a DC-DC converter in an EV is to take the high voltage from the main battery pack and convert it into a lower, stable voltage (typically 12 volts) that is needed to power the car’s accessories, such as lights, infotainment system, power windows, and the 12V battery.
Why do EVs need a 12V battery if they have a big high-voltage battery?
EVs still need a 12V battery to start up the vehicle’s electronic control units (ECUs) and computer systems before the main high-voltage battery is engaged. The DC-DC converter keeps this 12V battery charged from the main battery.
Can I drive my EV if the DC-DC converter fails?
In many cases, if the DC-DC converter fails, essential vehicle functions that rely on the 12V system will stop working, making the car undrivable or unsafe to operate. Warning lights on the dashboard will typically indicate such a failure.
Does the DC-DC converter affect my EV’s driving range?
Yes, indirectly. An efficient DC-DC converter minimizes energy loss during voltage conversion. This means more energy from the main battery is available to power the electric motor, thus helping to maximize the vehicle’s driving range.
Are DC-DC converters in EVs different from those in gasoline cars?
Yes, they are. In gasoline cars, the alternator (driven by the engine) handles the 12V power. In EVs, the DC-DC converter draws power from the much larger high-voltage battery to supply the 12V system, offering greater efficiency and decoupling power for accessories from engine operation.
<div
